BIOLOGICAL ASSOCIATION
Note Description
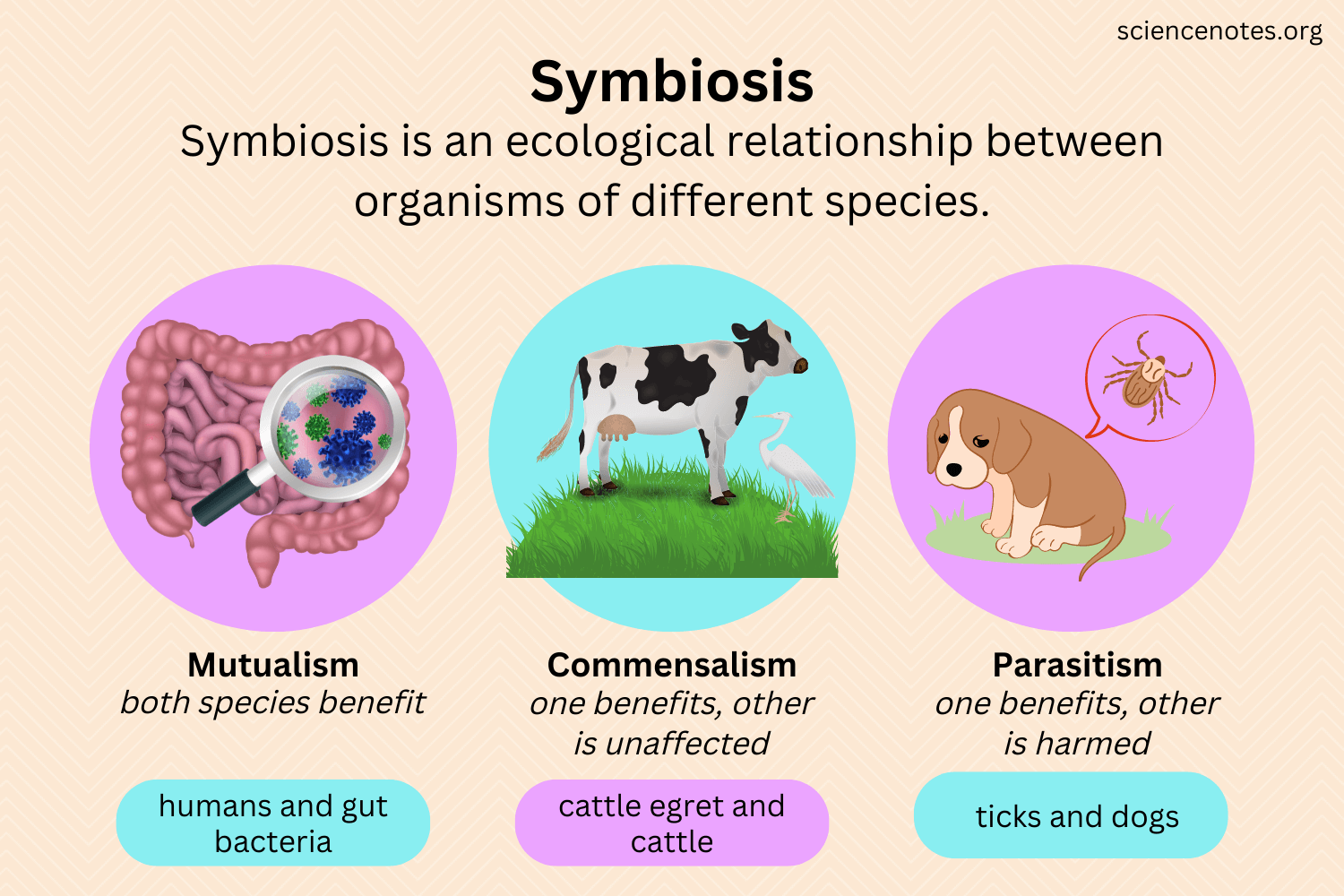
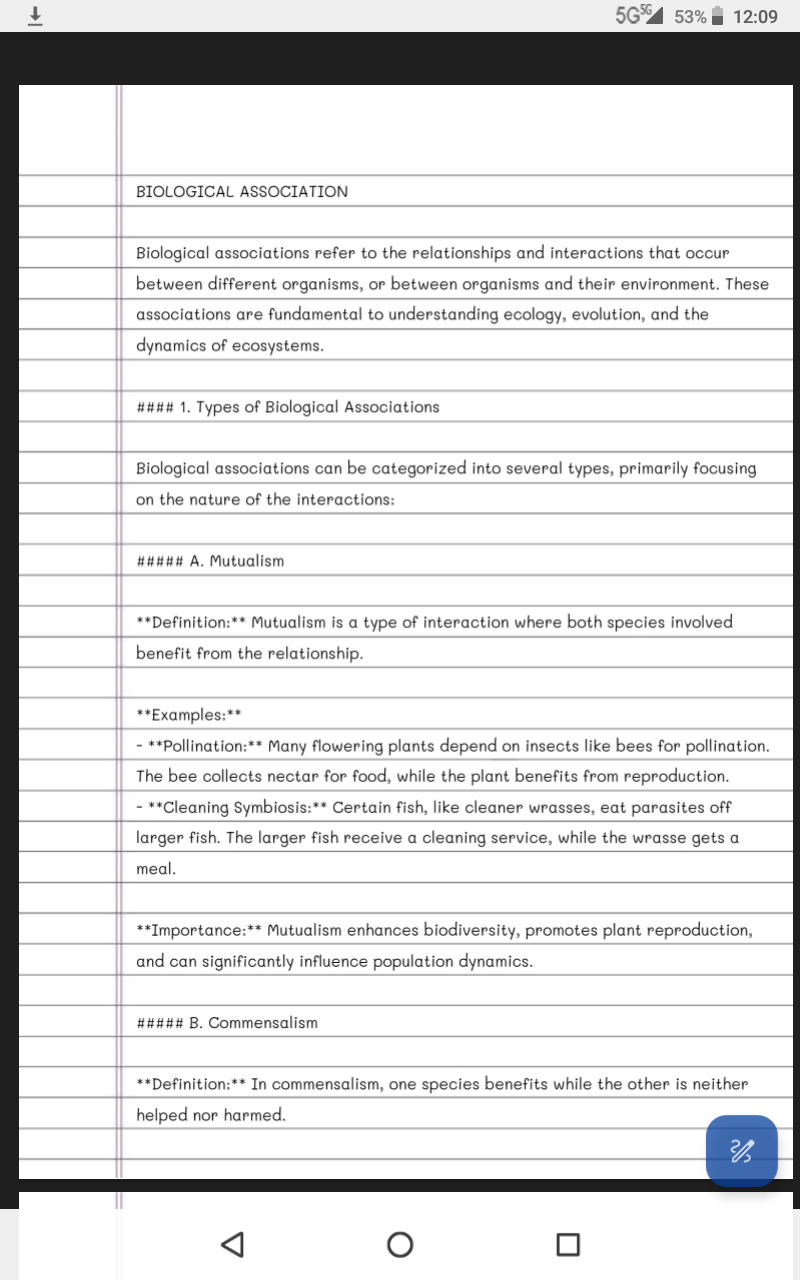
Biological associations, also known as symbiotic relationships, refer to the interactions between different species that live together in a community. These relationships can be mutually beneficial (mutualism), beneficial to one and harmful to the other (parasitism), or beneficial to one and neutral to the other (commensalism). Examples include clownfish and sea anemones (mutualism), tapeworms and hosts (parasitism), and remora fish and sharks (commensalism). These associations play a crucial role in shaping ecosystems, influencing species evolution, and maintaining biodiversity, demonstrating the intricate web of dependencies within the natural world.
...
Notes information
| Seller Price | GHC 0 |
| Added | 14 Oct, 2024 |
| University | Liberty Preparatory School |
| Course | Science |